Wheels and castors for food processing industries
The safety and ease of handling of a trolley depend on the choice of the most suitable wheel. The choice must be made in accordance with the following procedure:
Identify the use in order to define the essential wheel requirements in terms of materials, strength and performance.
The maximum load capacity of wheels for industrial use is expressed in daN and defined by tests carried out in accordance with the ISO 22883:2004 standard. The maximum load capacity is determined by tests carried out in accordance with the ISO 22881:2004 standard for institutional wheels and castors, and with the ISO 22879:2016 or ISO 22880:2016 standards for castors for furniture
To calculate the load capacity required for the specific application, it is necessary to consider the weight of the vehicle, the number of wheels in contact with the ground and the position of the load relative to the centre of gravity.
Solid load:
on a trolley with four wheels in motion, only three wheels are always load-bearing.
Liquid load::
on a trolley with four wheels in motion, only two wheels are load-bearing due to the oscillating movement of the liquid.
The wheel performance values indicated in the Tellure R ta documentation refer to intermittent handling. In the case of continuous handling requirements, please contact us for further information.
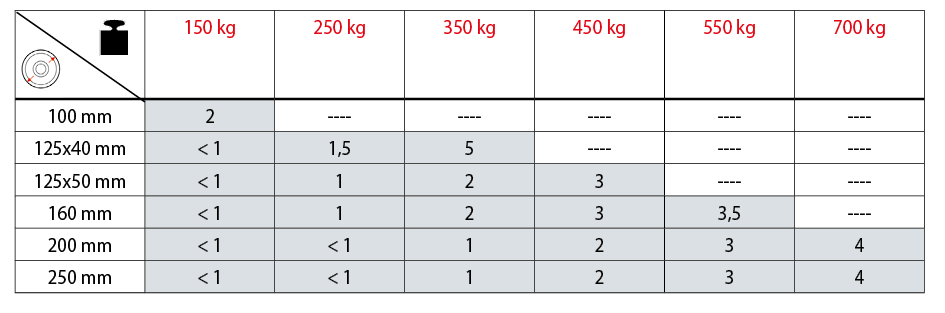
The catalogue includes a table for each wheel series indicating the pushing or pulling force required to move the load, as shown in the example below.
For each load and diameter, the table indicates the force (in daN) required to push or pull a single wheel at a constant speed of 4 km/h on a smooth floor. For manual handling of a 4-wheel trolley, choose values < 5 daN; for frequent handling, choose values < 3 daN.
It is necessary to consider that the wheel s load capacity is reduced at higher speeds, with percentages varying based on the type of covering.
For high-speed applications (above 6 km/h), wheels covered in cast polyurethane combined with electrowelded castors are recommended.
This table shows only wheel types recommended by Tellure Rota for use above 4 km/h. For other products, mechanical handling above 4 km/h is not recommended
For speeds above 4 km/h, the use of wheels with ball bearing hubs combined with medium-heavy duty P-PX, mheavy-duty with hardned ball race grooves PT, extra heavy EP, electrowelded EE MHD, EE HD, EE EHD, twin electrowelded EEG MHD, EEG HD, EEG EHD and sprung loaded electrowelded EES MHD brackets are recommended.
Light-duty SL, standard-duty NL, NLX, and medium-duty M are not recommended above 4 km/h for mechanical handling.
Download PDFCheck the compatibility of each series with the different types of flooring and the environmental conditions indicated in the documentation.
For each series, check compatibility with the main families of chemical agents present.
In the presence of water, oil, grease or corrosive substances, it is necessary to select wheels and castors made of resistant materials in order to preserve performance and durability.
The ease with which the trolleys can o be driven and manoeuvred depends on the number and arrangement of the wheels, the type of castors and the position of the load s centre of gravity, all of which must be carefully evaluated to determine the most suitable mounting configuration.
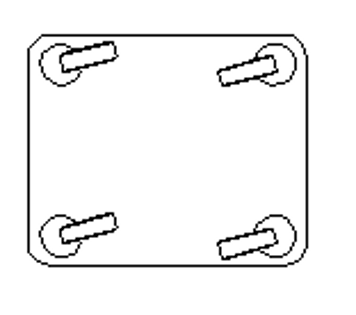
They ensure maximum manoeuvrability: the trolley can rotate on its own axis and change direction very easily, although with reduced control.
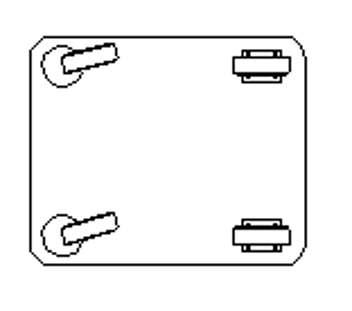
Recommended solution for long straight routes and medium loads with manual traction, allowing the trolley to turn around its longitudinal axis while maintaining good directional stability.
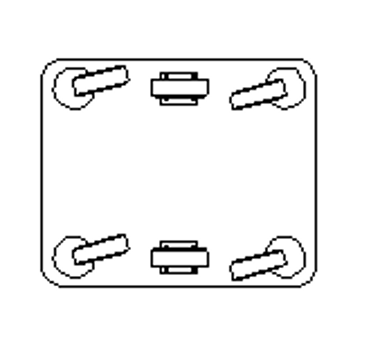
Very high load capacity and stability, combined with excellent straight-line guidance and the ability for the trolley to rotate on itself. This is the ideal solution for very heavy loads and very long trolleys.
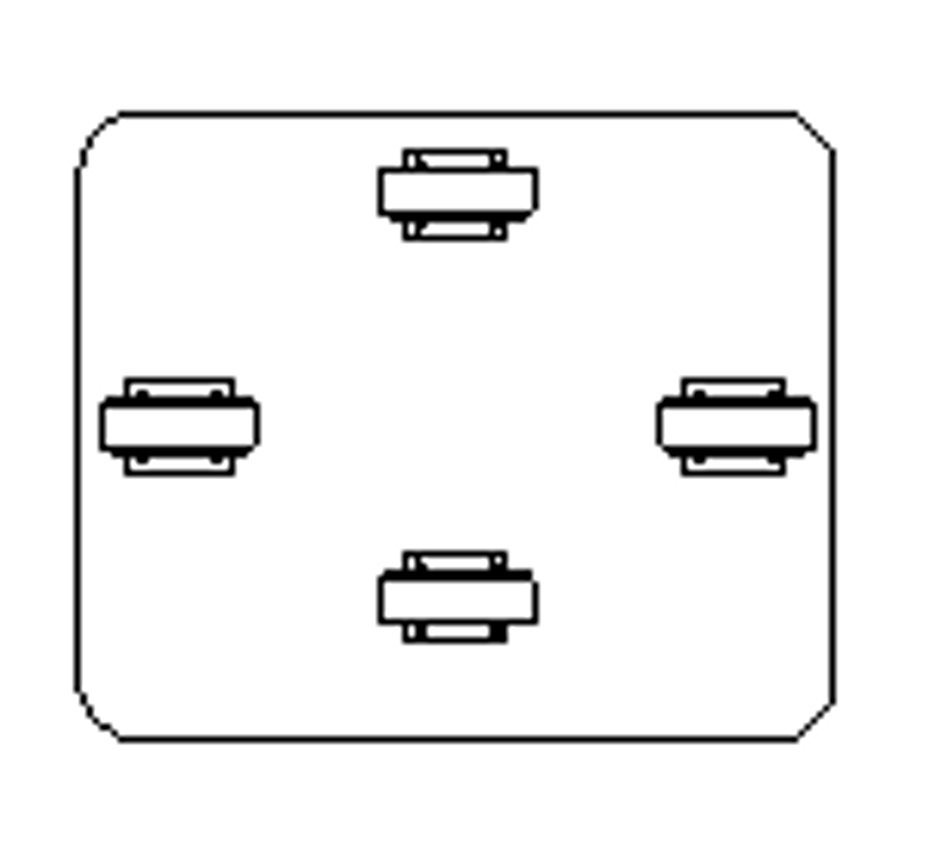
Suitable for long straight routes with no changes of direction.
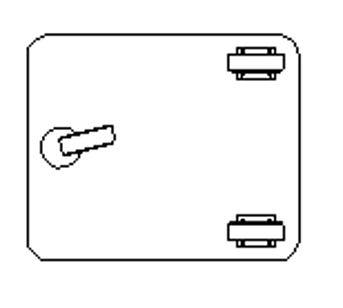
Suitable for long straight routes with few direction changes.
The amount of energy required to keep a wheel moving increases with load and with axle and rolling friction, but decreases as the wheel diameter increases.
Choosing large-diameter wheels with appropriate compounds improves rolling resistance and reduces energy consumption.